The Main Function Of The Mononuclear Phagocyte System Is To Provide
The main function of the mononuclear phagocyte system is to provide. The mononuclear phagocyte system has two specific functions. Mononuclear phagocytes including monocytes and macrophages are a central component of the hosts innate immune system designated to protect against invading pathogens. Due to the involvement of phagocytes the RES is also known as the mononuclear phagocyte system MPS.
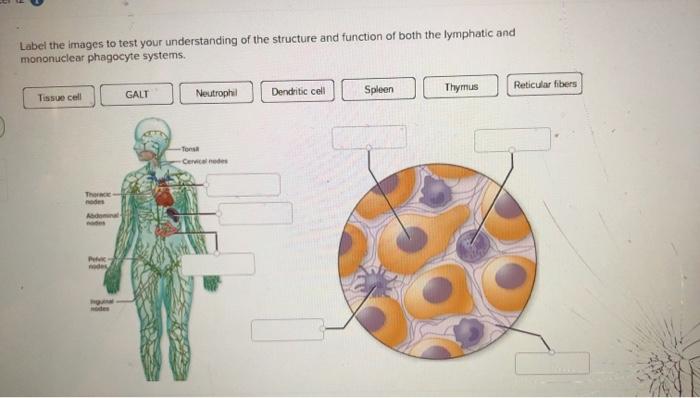
Macrophages are a major cell population in most of the tissues in the body and their numbers increase further in inflammation wounding and malignancy. The mononuclear phagocyte system is a heterogeneous group of leukocytes composed of tissue-resident macrophages dendritic cells and monocyte-derived cells that are critical in defense against. Filtration of extracellular fluid.
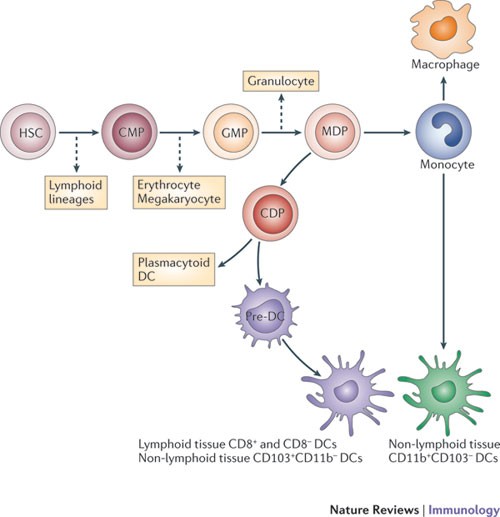
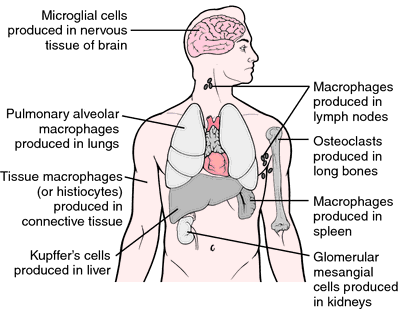
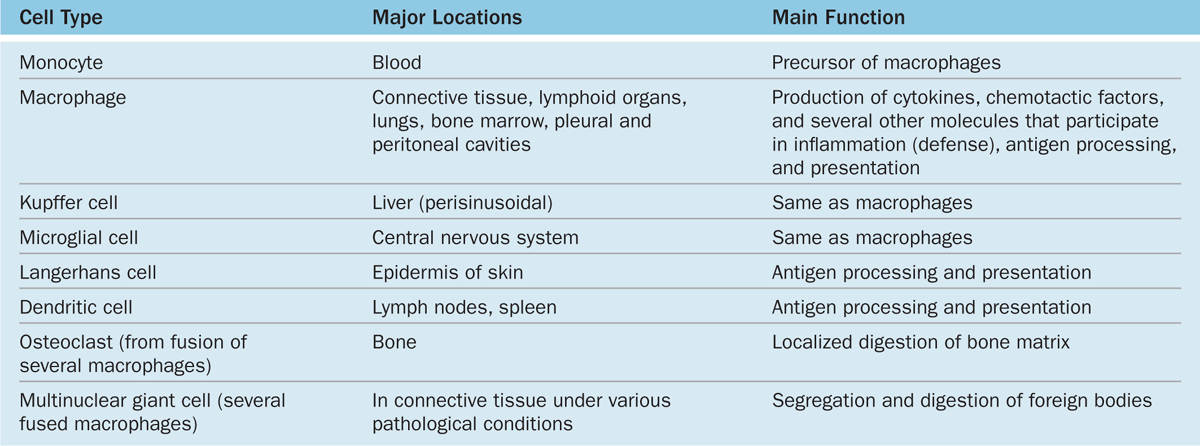
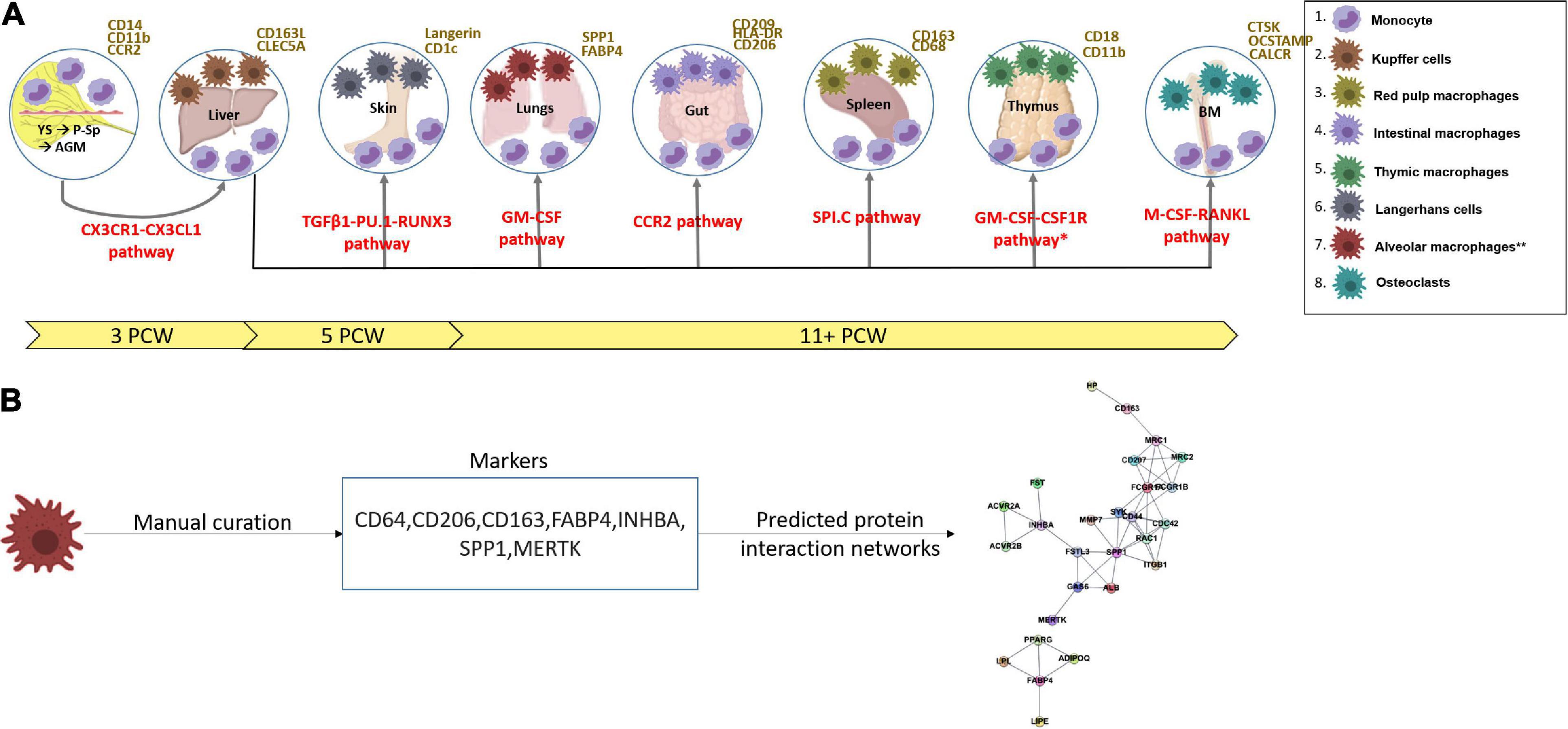
The mononuclear phagocyte system MPS has been defined as a family of cells comprising bone marrow progenitors blood monocytes and tissue macrophages. LocationConnective tissue lymphoid organs lungs bone marrow. One study demonstrated the cross-species preservation of the phenotypic and functional properties of CD103 DCs isolated from the human mesenteric LNs 7.
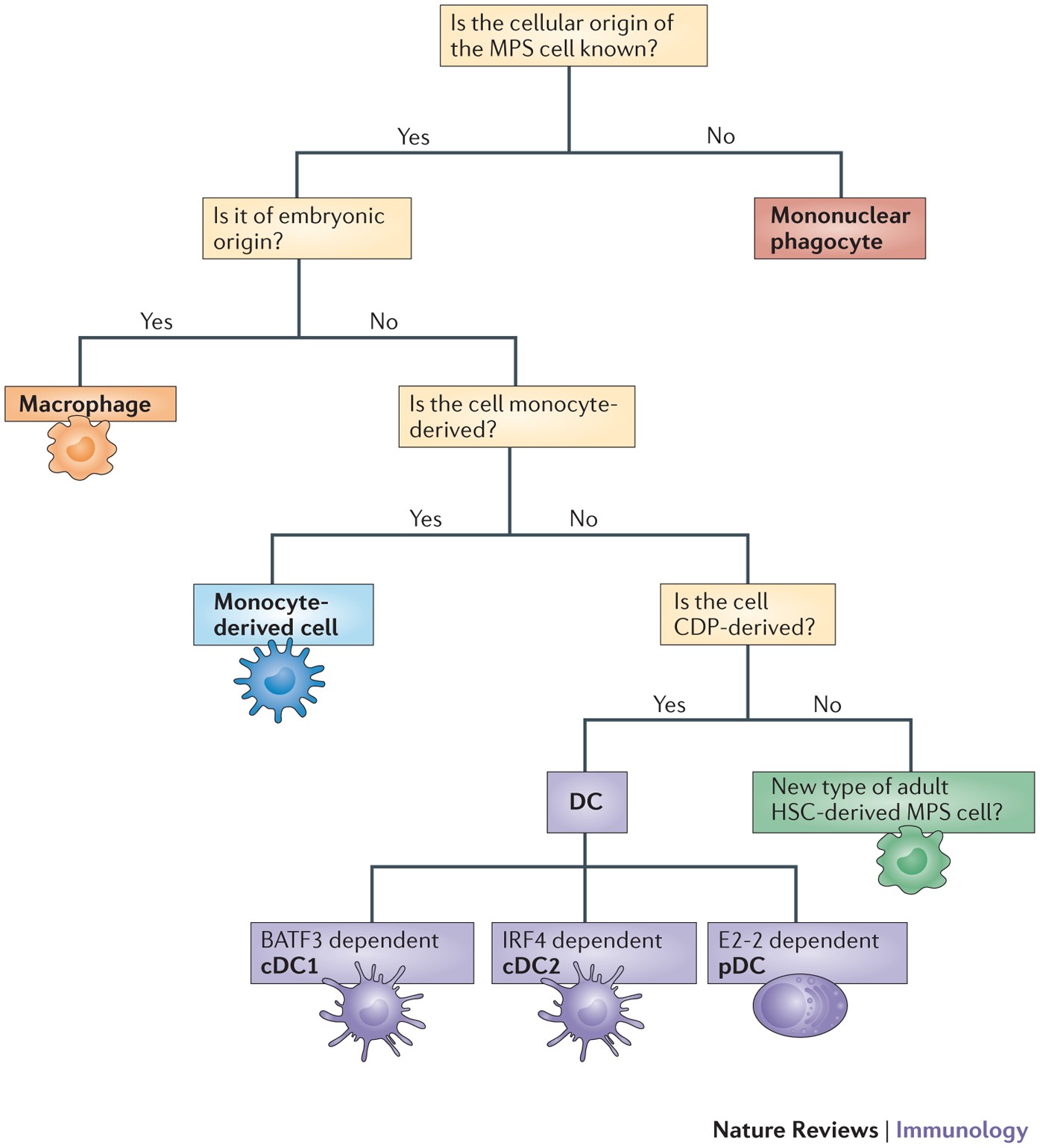
The main function of the mononuclear phagocyte system is to provide A. The main role of the RES is to identify foreign antigens and mount an appropriate immune response. The previously proposed phagocyte cell systems including the most recent and presently prevailing one the mononuclear phagocyte system MPS grouped mononuclear cells but excluded neutrophils creating an unacceptable situation.
However these cells do not only interact with various parts of the innate and adaptive immune system but also fulfill indispensable duties during the control of tissue homeostasis and organ function. Phagocytes are crucial in the host defense against microbial infection. Current knowledge concerning morphology histochemistry peroxydase and esterase activity immunology specific surface antigens receptors on the cell membranes function immune phagocytosis pinocytosis kinetics 3H-thymidine labelling and culture makes it possible to place all highly phagocytic mononuclear cells and their precursors in one system which is called the.
Mononuclear phagocytes including monocytes and macrophages are a central component of the hosts innate immune system designated to protect against invading pathogens. Their trophic roles for other cell types in. They detect and phagocytose pathogens recruit cells initiate adaptive immunity by presenting antigens to T cells and coordinate the resolution of inflammation and wound healing.
Hematopoietic stem cells blood monocytes and cells which are associated with the connective. The term mononuclear phagocyte system MPS was developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s by van Furth.
One study demonstrated the cross-species preservation of the phenotypic and functional properties of CD103 DCs isolated from the human mesenteric LNs 7.
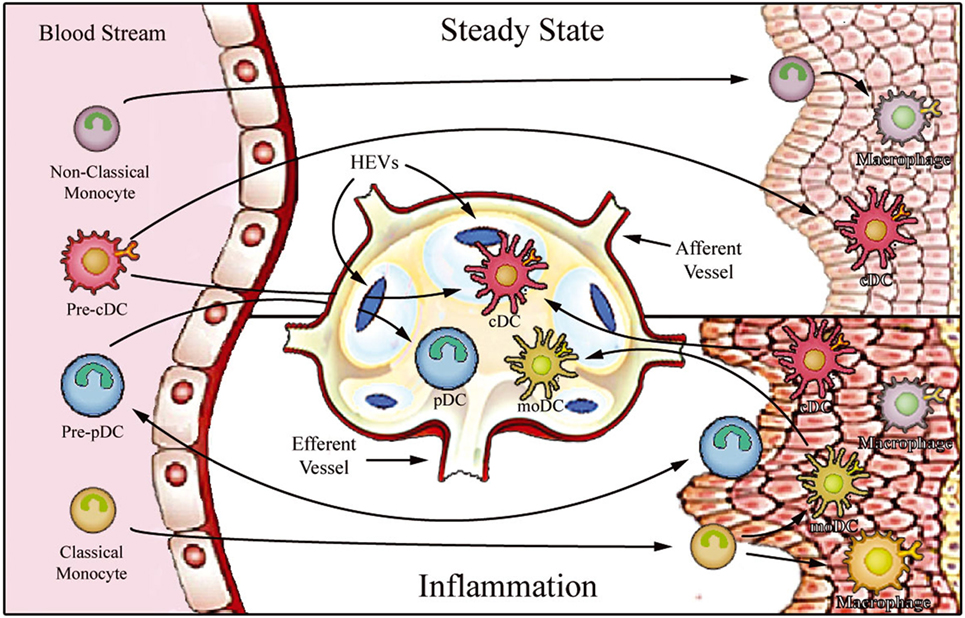
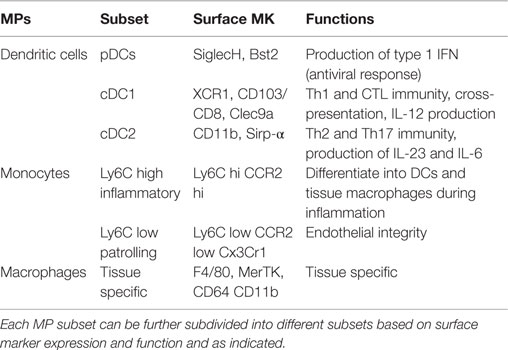
One study demonstrated the cross-species preservation of the phenotypic and functional properties of CD103 DCs isolated from the human mesenteric LNs 7. Mononuclear phagocytes including monocytes and macrophages are a central component of the hosts innate immune system designated to protect against invading pathogens. Phagocytosis is important in nonspecific clearance of foreign antigens. Mononuclear phagocyte system present in bone marrow consists of various forms of monocytes and macrophages which perform various major functions like phagocytosis destruction clearance of microorganisms and apoptotic cells chemotaxis secretion of enzymes antigen processing and destruction of tumor cells. A role for heme oxygenase-1 Antioxid Redox Signal. The MPS encompasses monocytes dendritic cells DCs and macrophages and altogether they play vital roles in tissue development maintenance of homeostasis inflammation and the innate immune defense against pathogens. The mononuclear phagocyte system in homeostasis and disease. Phagocytes are crucial in the host defense against microbial infection. Hematopoietic stem cells blood monocytes and cells which are associated with the connective.
A role for heme oxygenase-1 Antioxid Redox Signal. The mononuclear phagocyte system has two specific functions. One study demonstrated the cross-species preservation of the phenotypic and functional properties of CD103 DCs isolated from the human mesenteric LNs 7. The term mononuclear phagocyte system MPS was developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s by van Furth. However these cells do not only interact with various parts of the innate and adaptive immune system but also fulfill indispensable duties during the control of tissue homeostasis and organ function. The mononuclear phagocyte system is a heterogeneous group of leukocytes composed of tissue-resident macrophages dendritic cells and monocyte-derived cells that are critical in defense against. The mononuclear phagocyte system MPS has been defined as a family of cells comprising bone marrow progenitors blood monocytes and tissue macrophages.




























Post a Comment for "The Main Function Of The Mononuclear Phagocyte System Is To Provide"