Respiratory System And Homeostasis
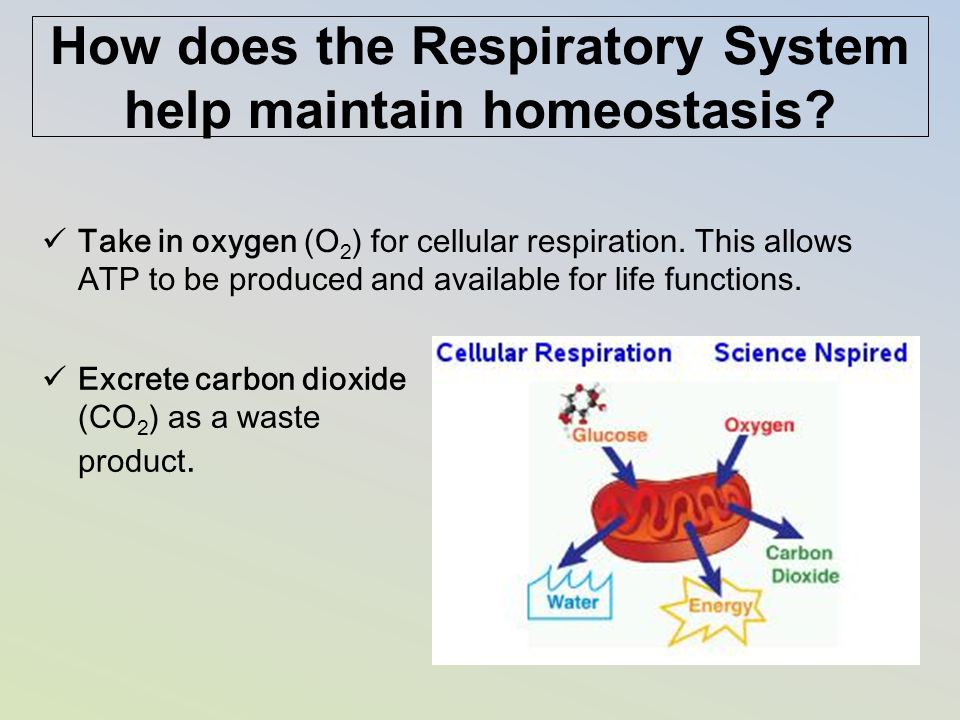
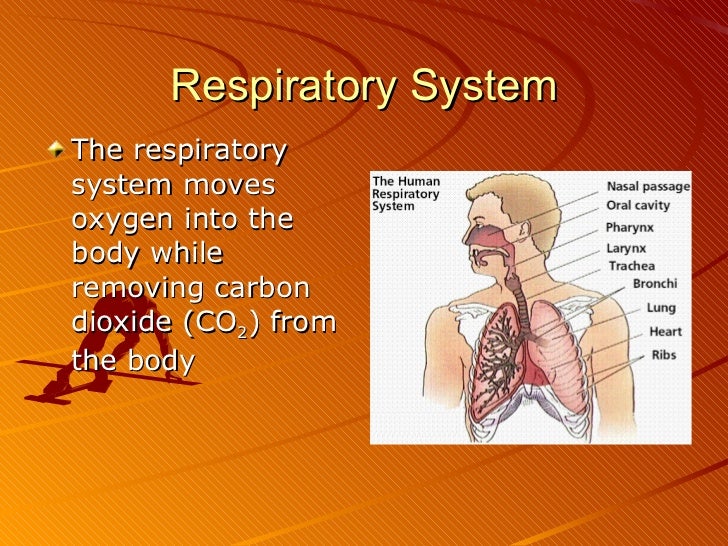
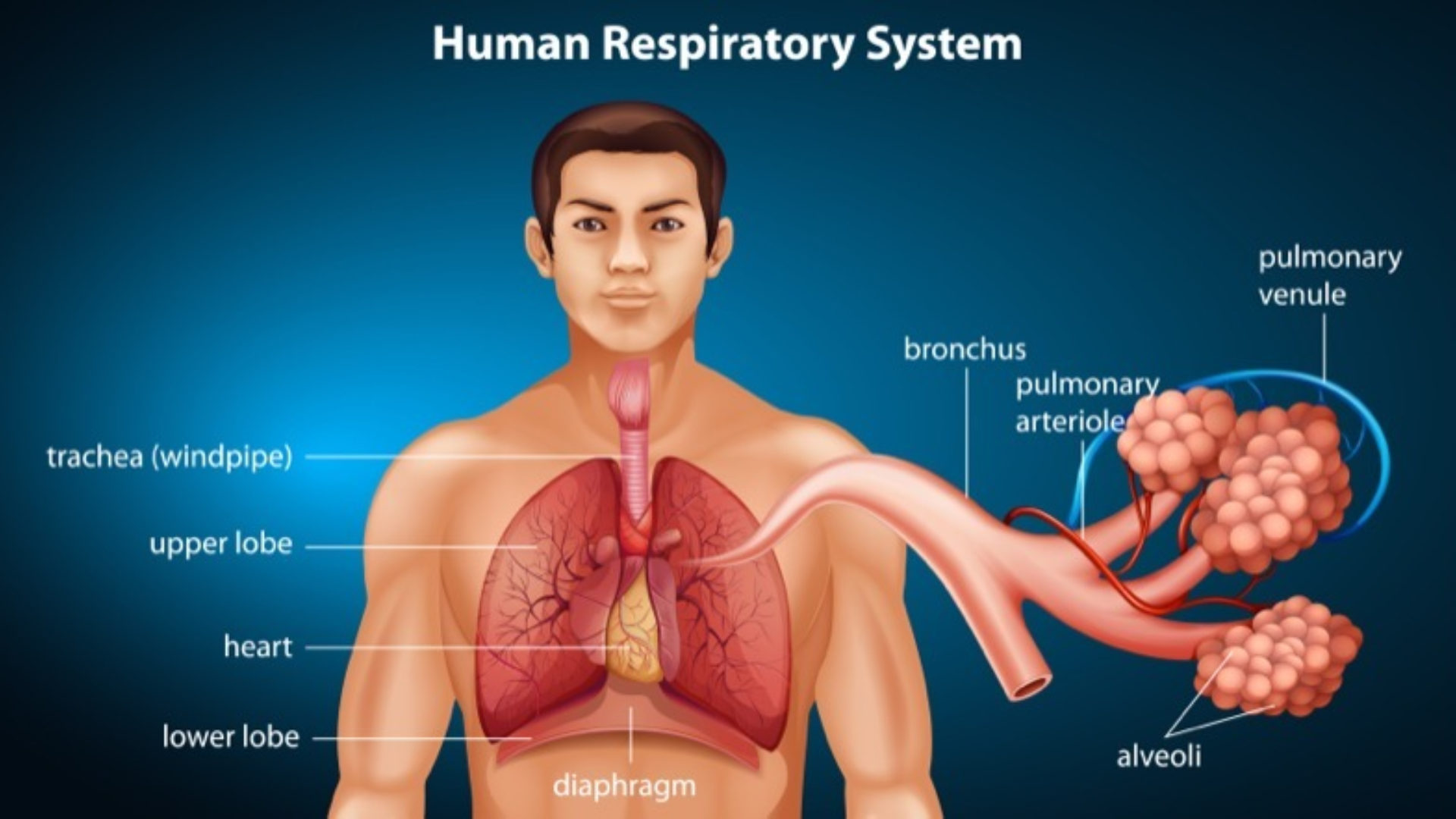
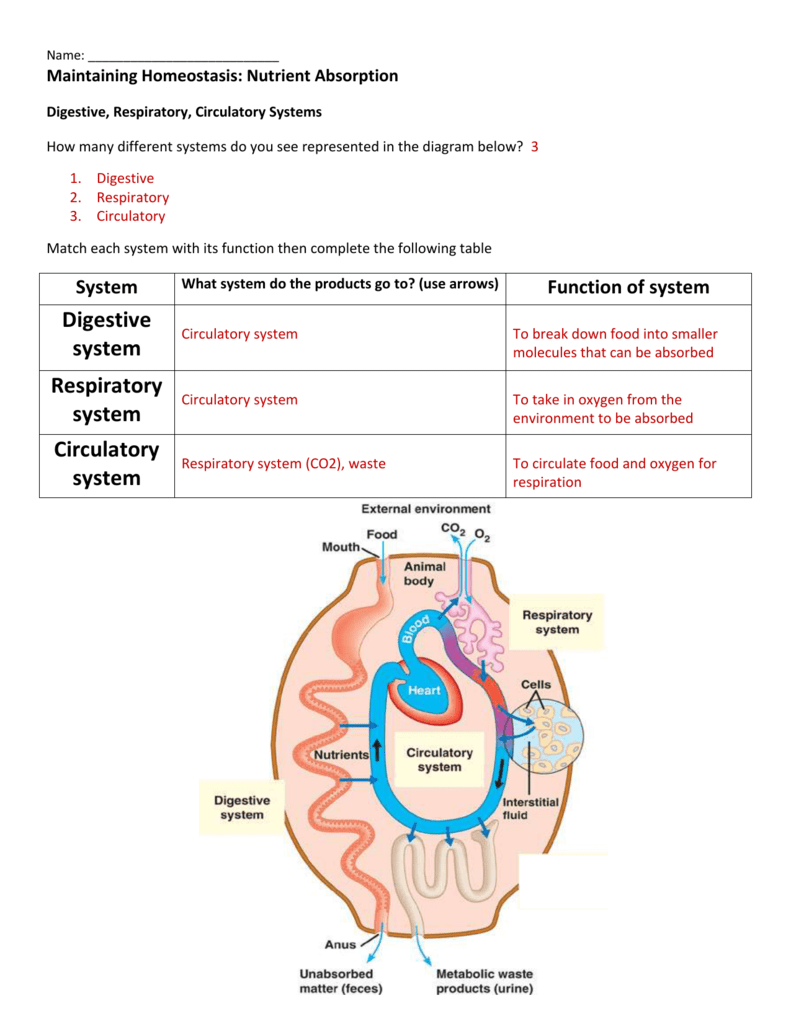
Respiratory system and homeostasis. Thus the Respiratory and Circulatory system work together in gas exchange which is vital in Homeostasis. Two lesser known processes involve the respiratory system and homeostasis. The primary organs of the respiratory system are the lungs which function to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide as we breathe.
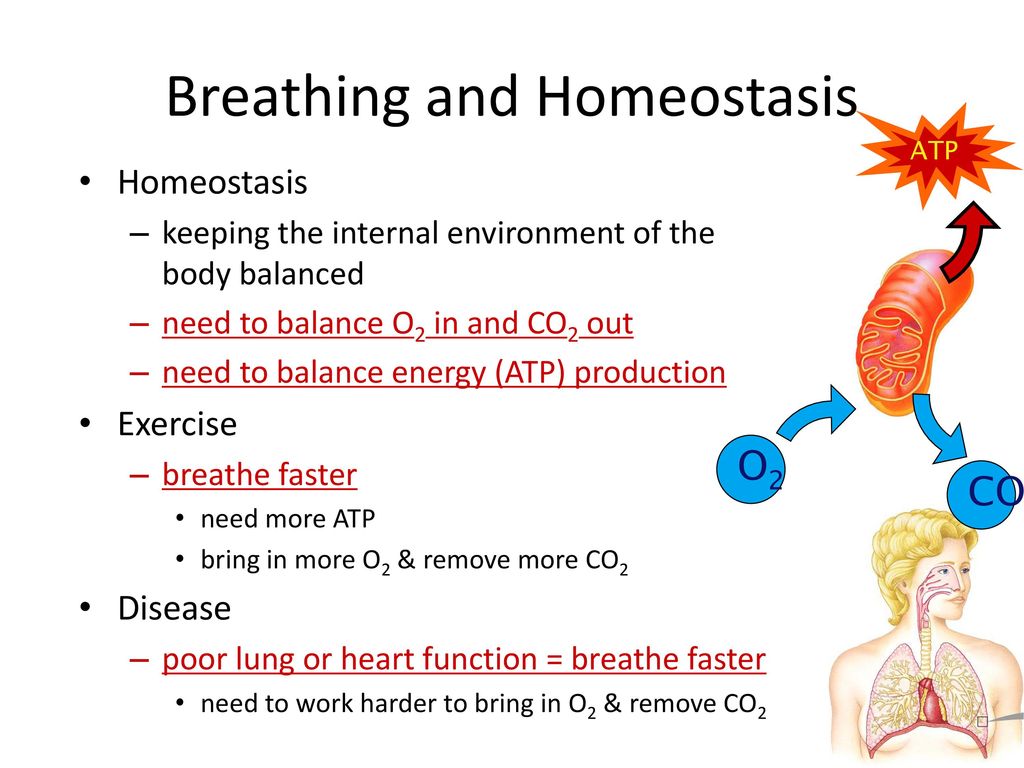
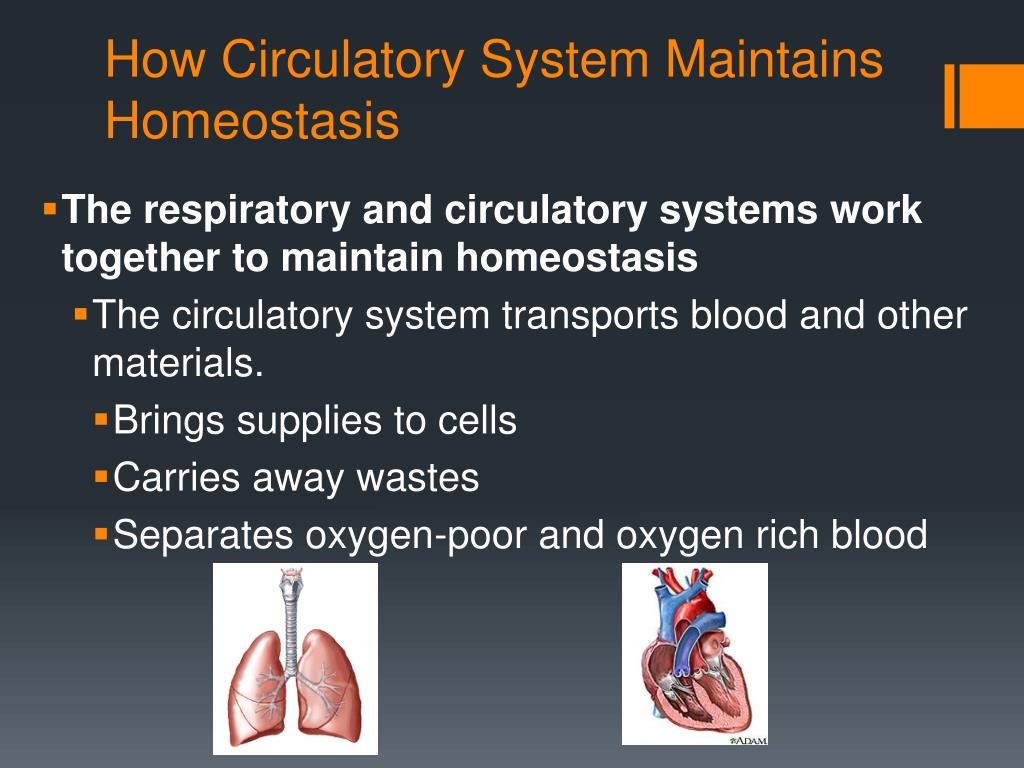
As the human body having ability of inhalation and exhalationOxygen go intoin the body of human body and carbon dioxide move outside of human Bodyin such away it. The respiratory system works hand-in-hand with the nervous and cardiovascular systems to maintain homeostasis in blood gases and pH. Lungs and the respiratory system help by balancing out the gases in our bodies.
Homeostasis comprises dynamic processes that enable optimum conditions to be maintained for cells in spite of continual changes taking place internally and externally. As in atmosphere which is mixture of gases. Homeostasis is the overall equilibrium of the bodys internal organs and functions.
Eitherif we say about respiratory system that how it relates with homeostasis. Respiration is one of the many body systems which are regulated by homeostatic processes. This chapter describes this process and gives an example of how it can be affected by ill health.
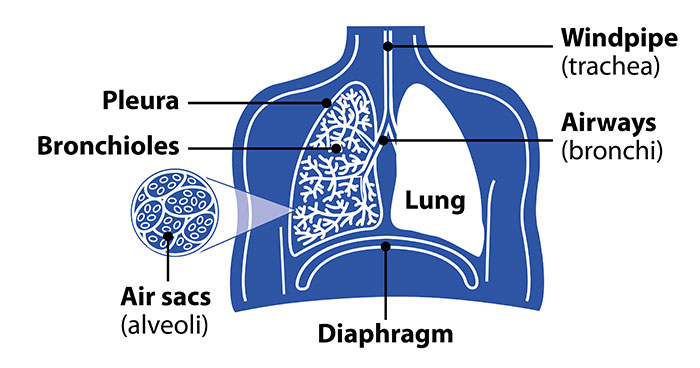
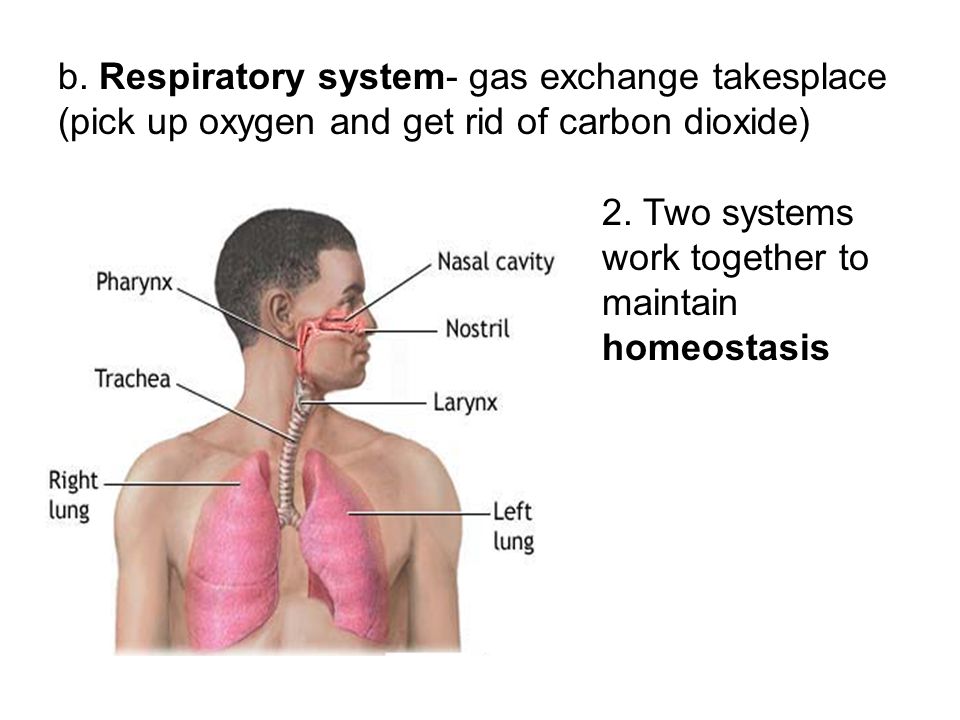
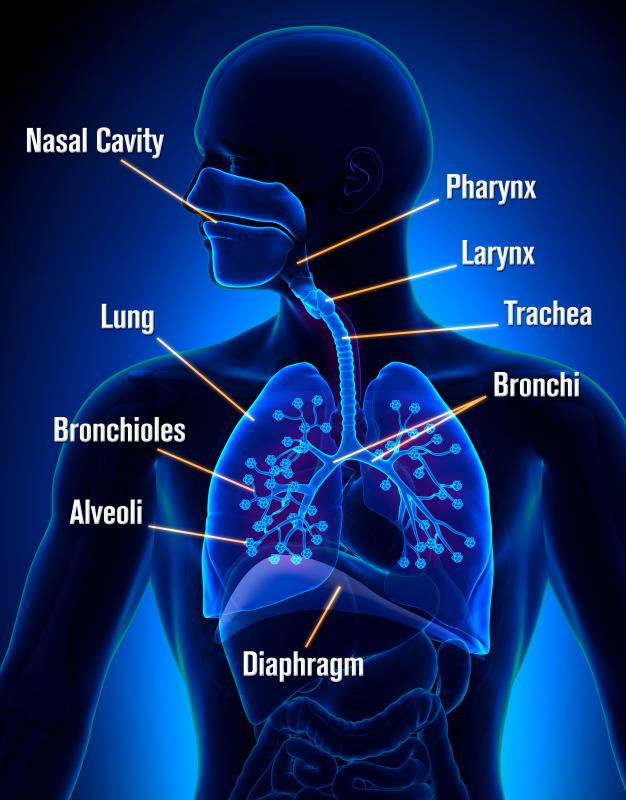
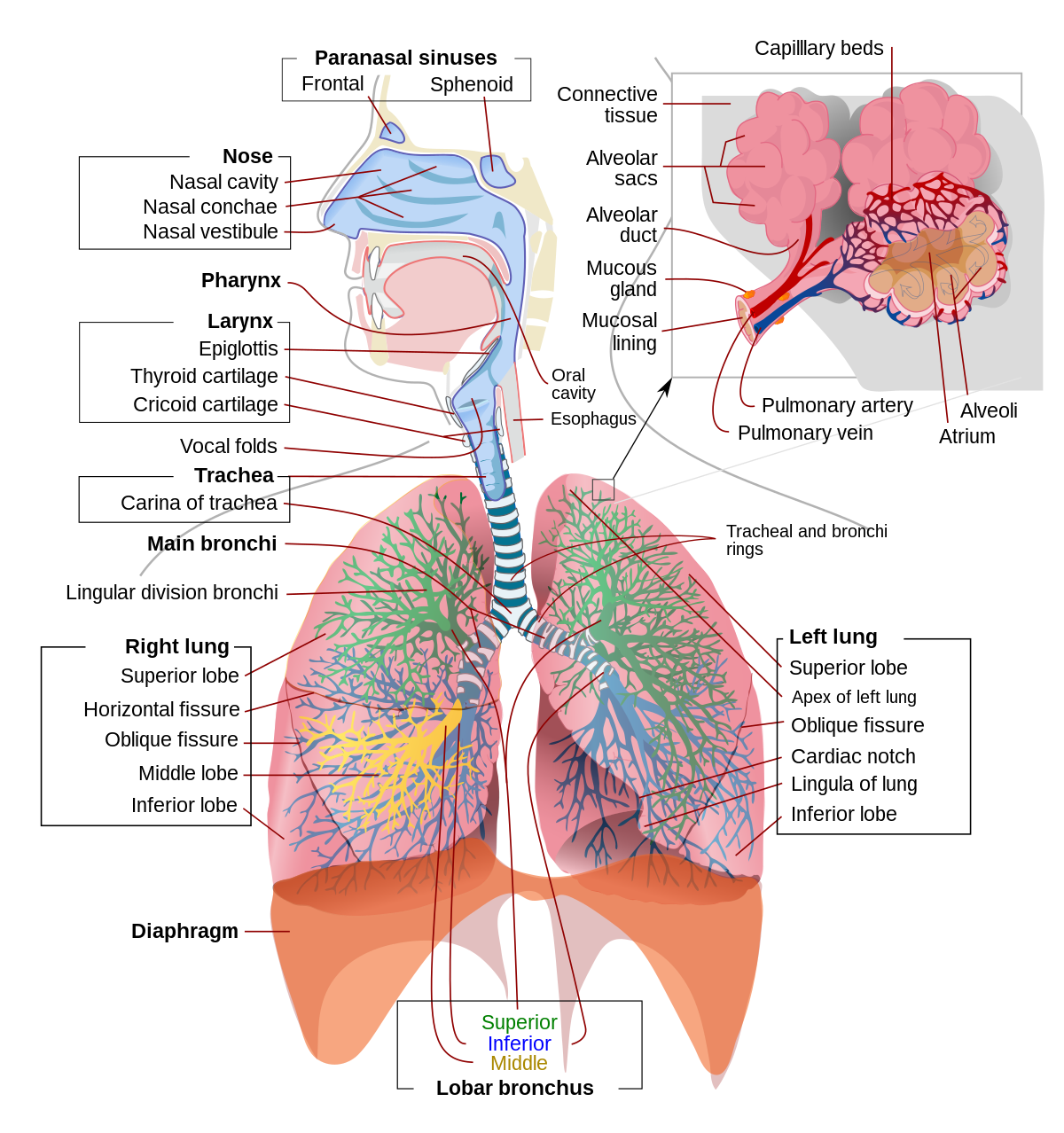
Included in the upper respiratory tract are the Nostrils Nasal Cavities. Homeostasis is all about getting the right balance and maintaining the correct balance is essential for our bodys survival. The primary physiologic functions of the respiratory system are to provide oxygen for cellular metabolic processes and to remove the gaseous waste product carbon dioxide.
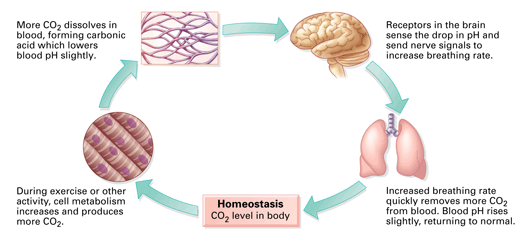
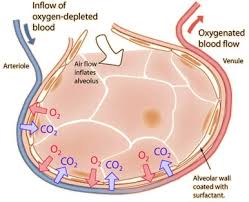
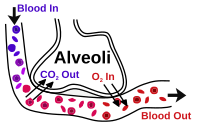
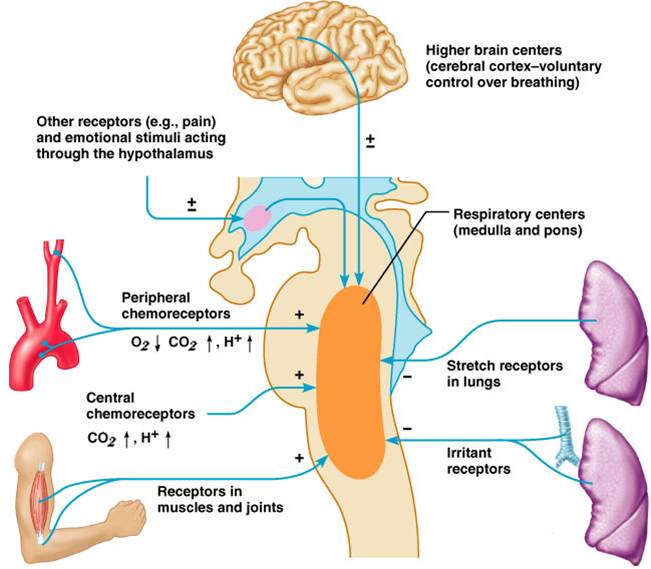
During exercise the respiratory system must work faster to keep the O 2 in the extracellular fluid and in the cells within normal limits preventing excessive build-up of CO 2 and disturbance to the blood pH. The organs of the respiratory system make sure that oxygen enters our bodies and carbon dioxide leaves our bodies. Luckily when we inhale plenty of oxygen enters our body through the.
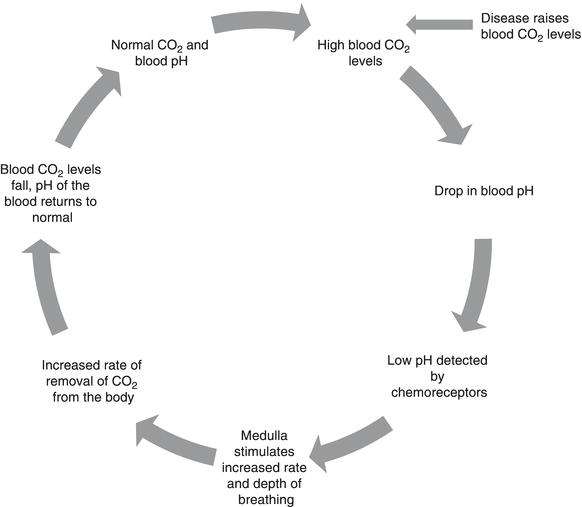
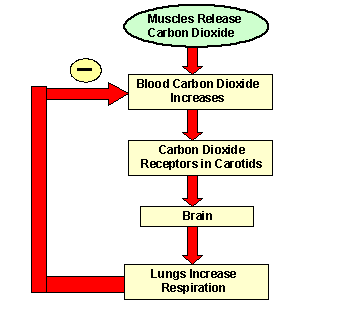
It is the level of carbon dioxide rather than the level of oxygen that is most closely monitored to maintain blood gas and pH homeostasis. In normal breathing there is a state of homeostasis.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply.
When there is an increased need for oxygen best observed during rigorous exercise our respiratory system responds with an increased rate and depth. P874 The respiratory system contributes to homeostasis by providing for the exchange of gases oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmospheric air blood and tissue cells. The respiratory system -- which comprises the nose the mouth the lungs and several other organs involved in breathing -- is involved in various important aspects of homeostasis. The organs of the respiratory system make sure that oxygen enters our bodies and carbon dioxide leaves our bodies. How does the respiratory system work. Homeostasis is all about getting the right balance and maintaining the correct balance is essential for our bodys survival. The Respiratory system allows entry of oxygen into the body and release Carbon Dioxide. Luckily when we inhale plenty of oxygen enters our body through the. Leave a Reply Cancel reply.
Homeostasis depends on the ability of your body to detect and oppose these changes. The respiratory tract is the path of air from the nose to the lungs. How does the respiratory system maintain homeostasis during exercise. This chapter describes this process and gives an example of how it can be affected by ill health. As the human body having ability of inhalation and exhalationOxygen go intoin the body of human body and carbon dioxide move outside of human Bodyin such away it. Respiratory homeostasis is concerned with the regulation of a blood gas composition that is compatible with maintaining cellular homeostasis. P874 The respiratory system contributes to homeostasis by providing for the exchange of gases oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmospheric air blood and tissue cells.
























Post a Comment for "Respiratory System And Homeostasis"