Monkey Disease In Humans
Monkey disease in humans. Risks from monkey bites include serious wound infections herpes B virus and rabies. Critical analyses of the relevance of monkey studies to human biology however indicate that this genetic similarity does not re. Monkeys in Malaysian forests are a reservoir for a rare form of malaria that could become a significant cause of disease in humans throughout South-East Asia a study warns.
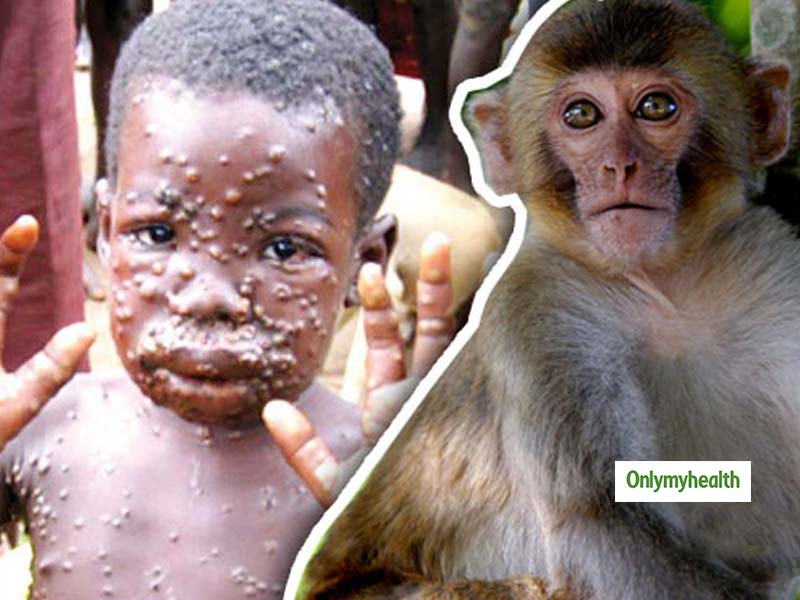
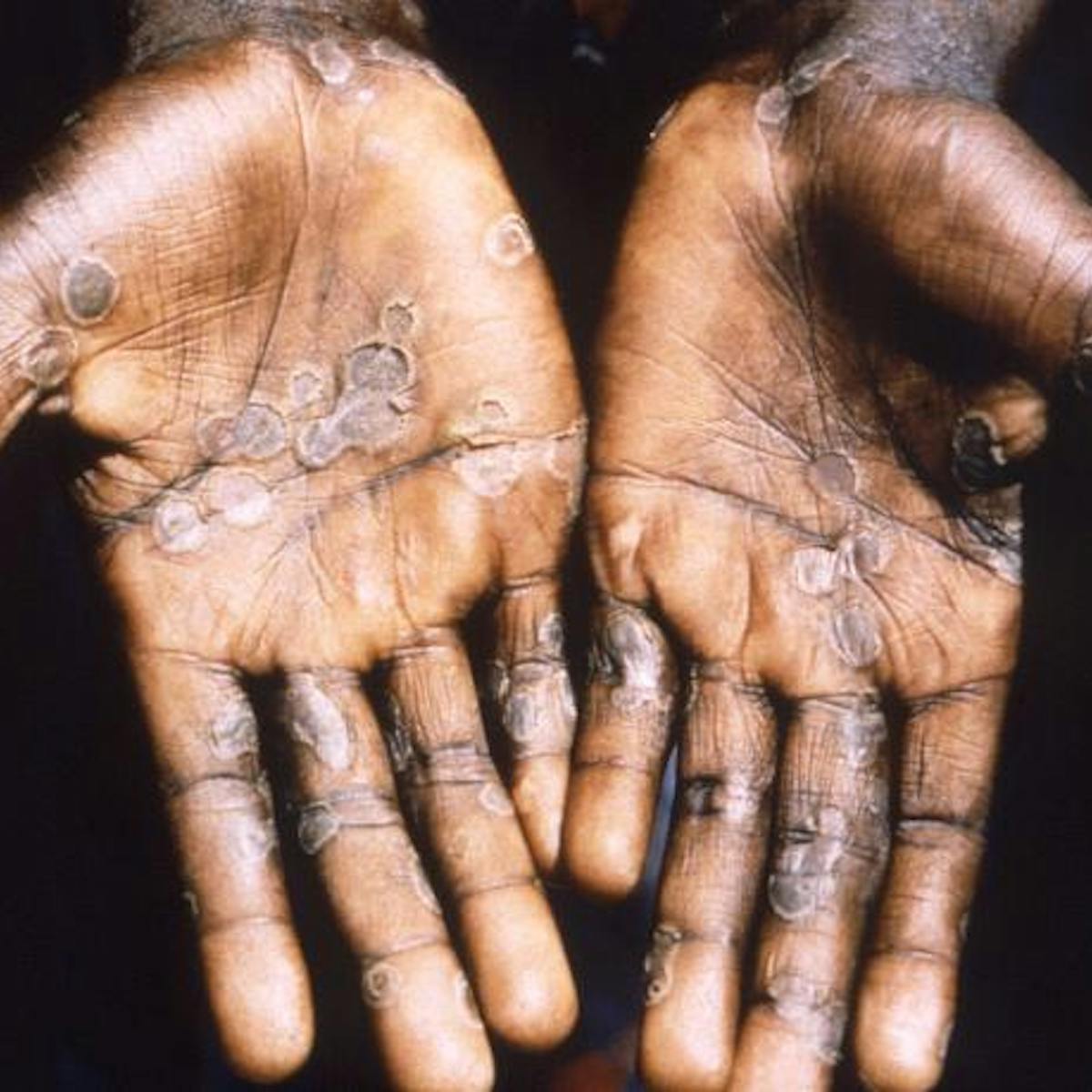
Many kinds pets can infect humans with salmonella including monkeys. This virus is a new type of adenovirus viruses that commonly affect people and cause colds flu-like symptoms and sometimes even death. 30 linhas Monkeypox is a rare disease that is caused by infection with monkeypox.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC unpub. Florida monkeys excreting rare disease that can kill humans scientists warn Wildlife agency says free-roaming monkeys at state park are a public health. Incubation periods may be as short as 2 days but more commonly are 2 to 5 weeks 1 3 5 - 7.
Herpes B virus usually transfers to humans through a bite or scratch or contamination with monkey saliva. Microscopy Gram-positive nonmotile acid-fast coccoid rods. Humans have become infected after exposure to infectious tissues or fluids of monkeys.
First isolated from monkeys in 1965. Strain ATCC 25276 CCUG 29115 CIP 106809 DSM. The ocular oral or genital secretions of monkeys as well as the central nervous system tissues and cerebrospinal fluid of monkeys are potentially infectious.
Salmonella Salmonella are bacteria that cause diarrhea in humans. Assertions that the use of monkeys to investigate human diseases is valid scientifically are frequently based on a reported 90-93 genetic similarity between the species. If a person is bitten or scratched by a monkey the wound should be thoroughly cleaned with soap and water.
Asiaticum can but rarely causes human pulmonary disease. Other diseases such as influenza and polio have gone the opposite route passing from humans to apes.
Other diseases such as influenza and polio have gone the opposite route passing from humans to apes.
Herpes B virus usually transfers to humans through a bite or scratch or contamination with monkey saliva. Humans have become infected after exposure to infectious tissues or fluids of monkeys. Strain ATCC 25276 CCUG 29115 CIP 106809 DSM. Incubation periods may be as short as 2 days but more commonly are 2 to 5 weeks 1 3 5 - 7. If a person is bitten or scratched by a monkey the wound should be thoroughly cleaned with soap and water. Other diseases such as influenza and polio have gone the opposite route passing from humans to apes. B-virus disease in humans usually results from macaque bites or scratches 4. Florida monkeys excreting rare disease that can kill humans scientists warn Wildlife agency says free-roaming monkeys at state park are a public health. Asiaticum can but rarely causes human pulmonary disease.
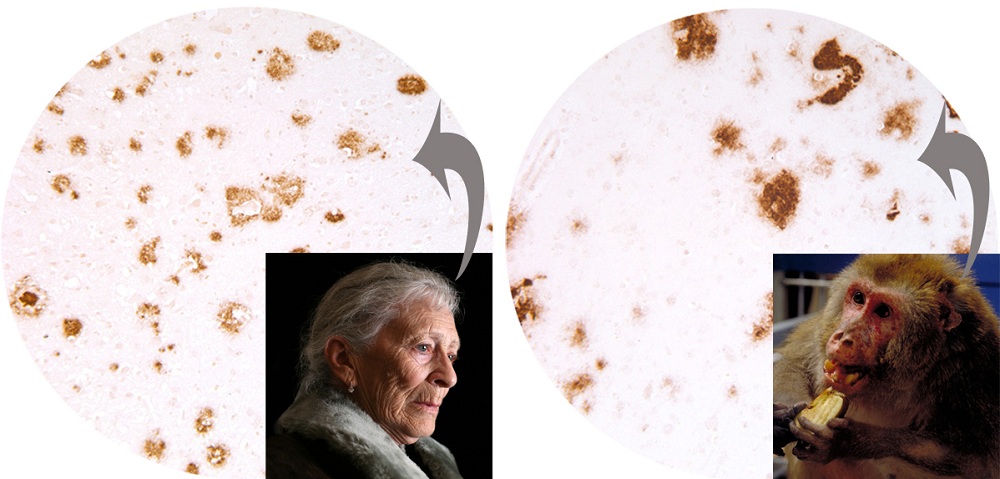
Microscopy Gram-positive nonmotile acid-fast coccoid rods. First isolated from monkeys in 1965. Breakthrough in the fight against Alzheimers as scientists develop new treatment that stops the disease progressing in monkey brains - and it could work in humans too. Salmonella Salmonella are bacteria that cause diarrhea in humans. Primary cell cultures derived from macaque kidneys are. Microscopy Gram-positive nonmotile acid-fast coccoid rods. The malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi is transmitted between monkeys by forest-dwelling mosquitoes.





















/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16026332/monkey_GettyImages_609576976__1_.jpg)


















Post a Comment for "Monkey Disease In Humans"