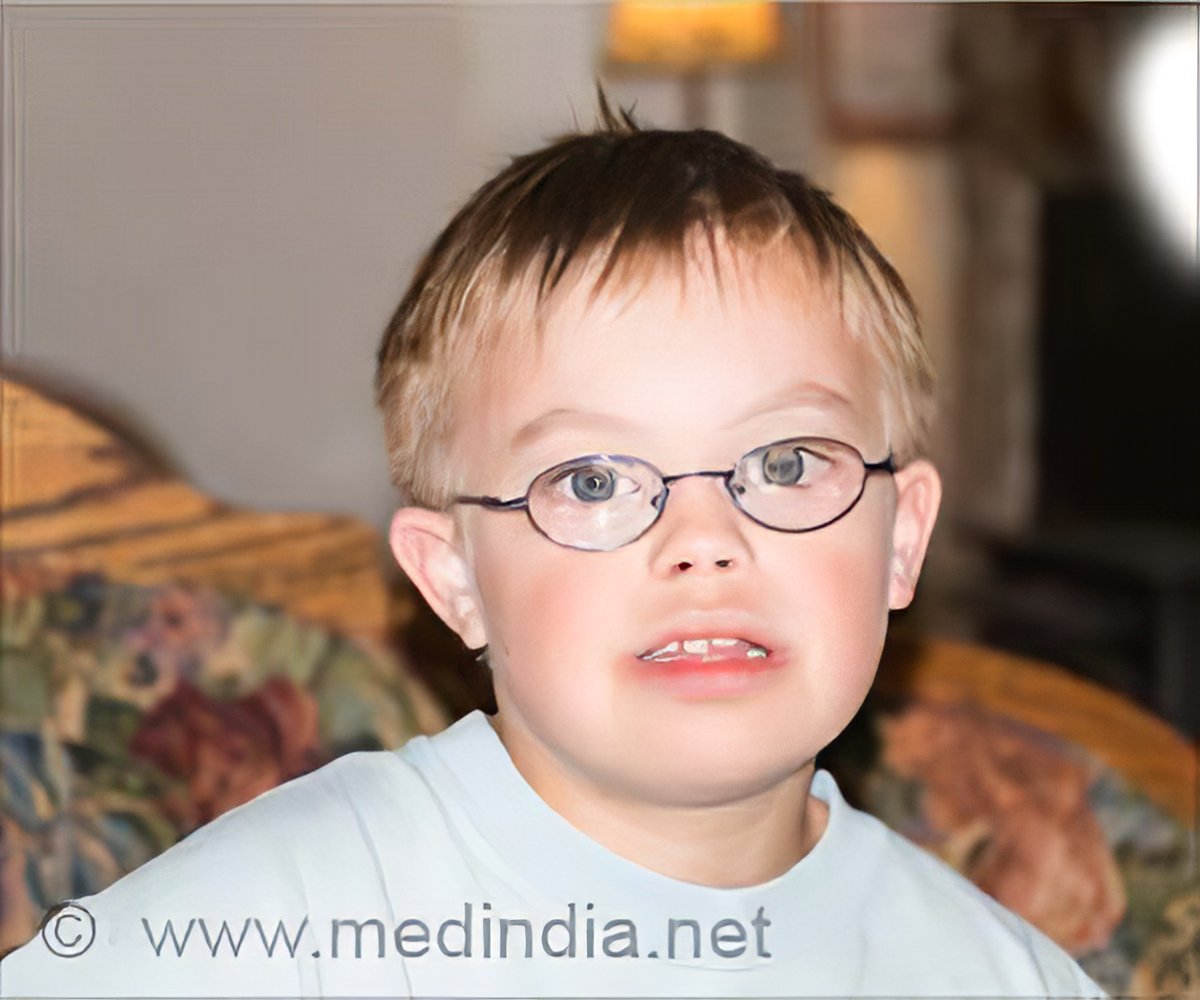
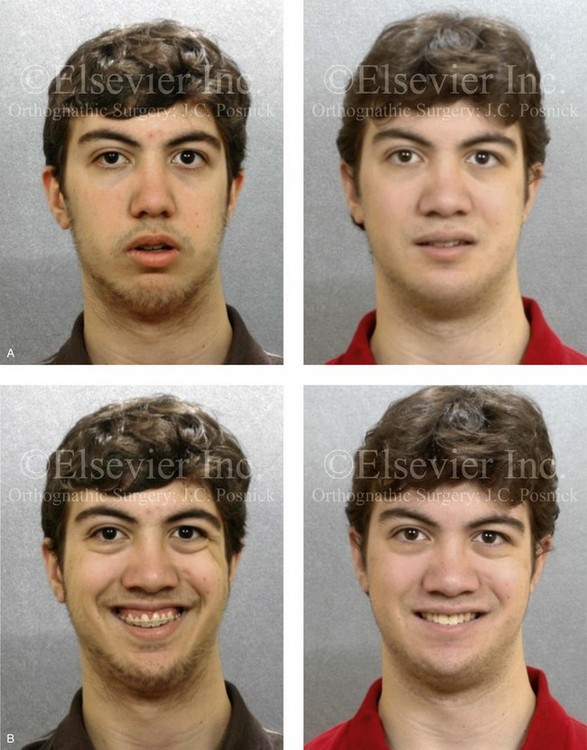
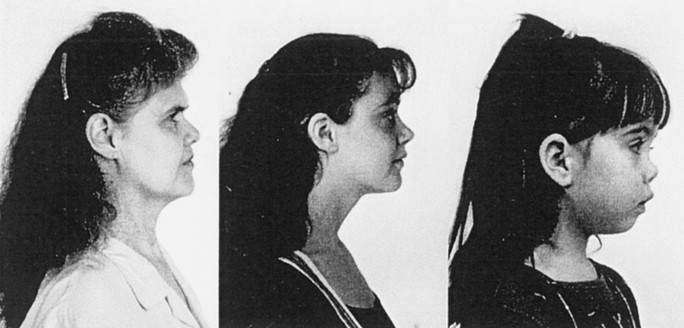
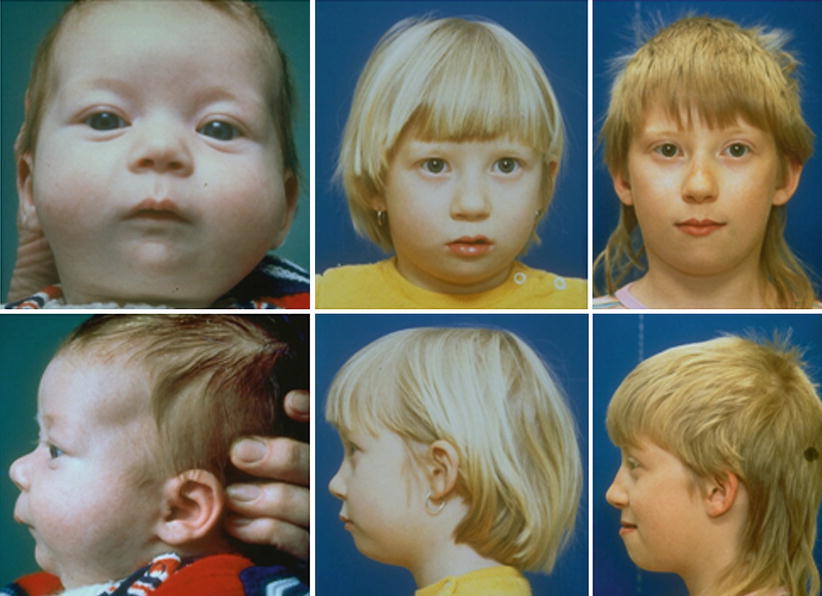
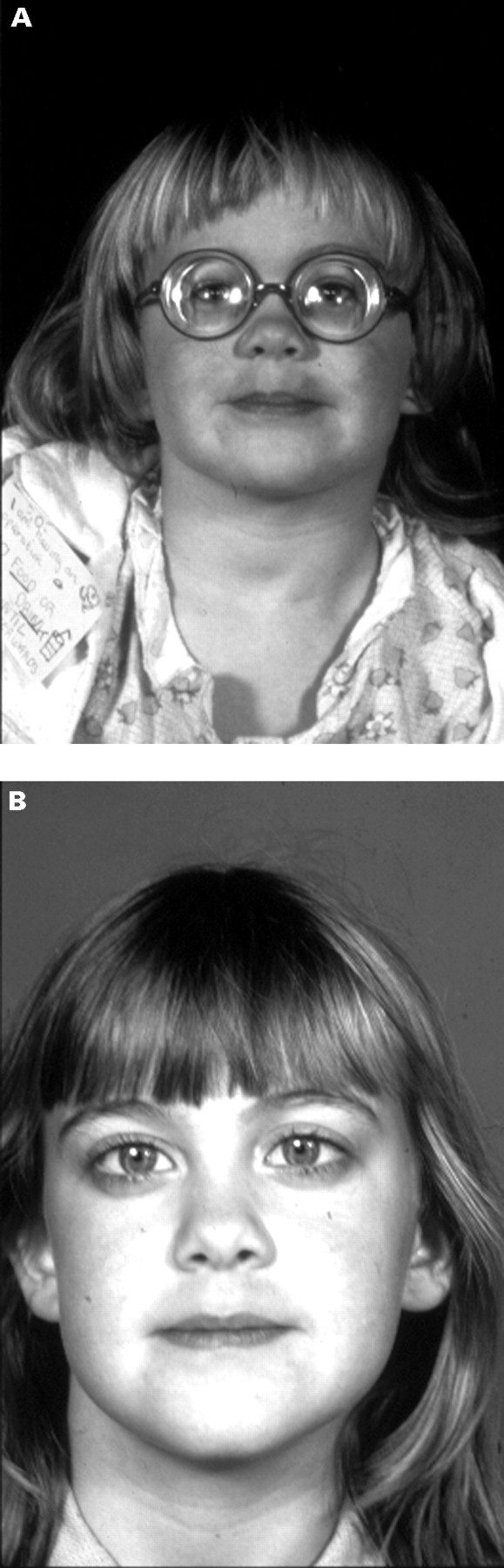
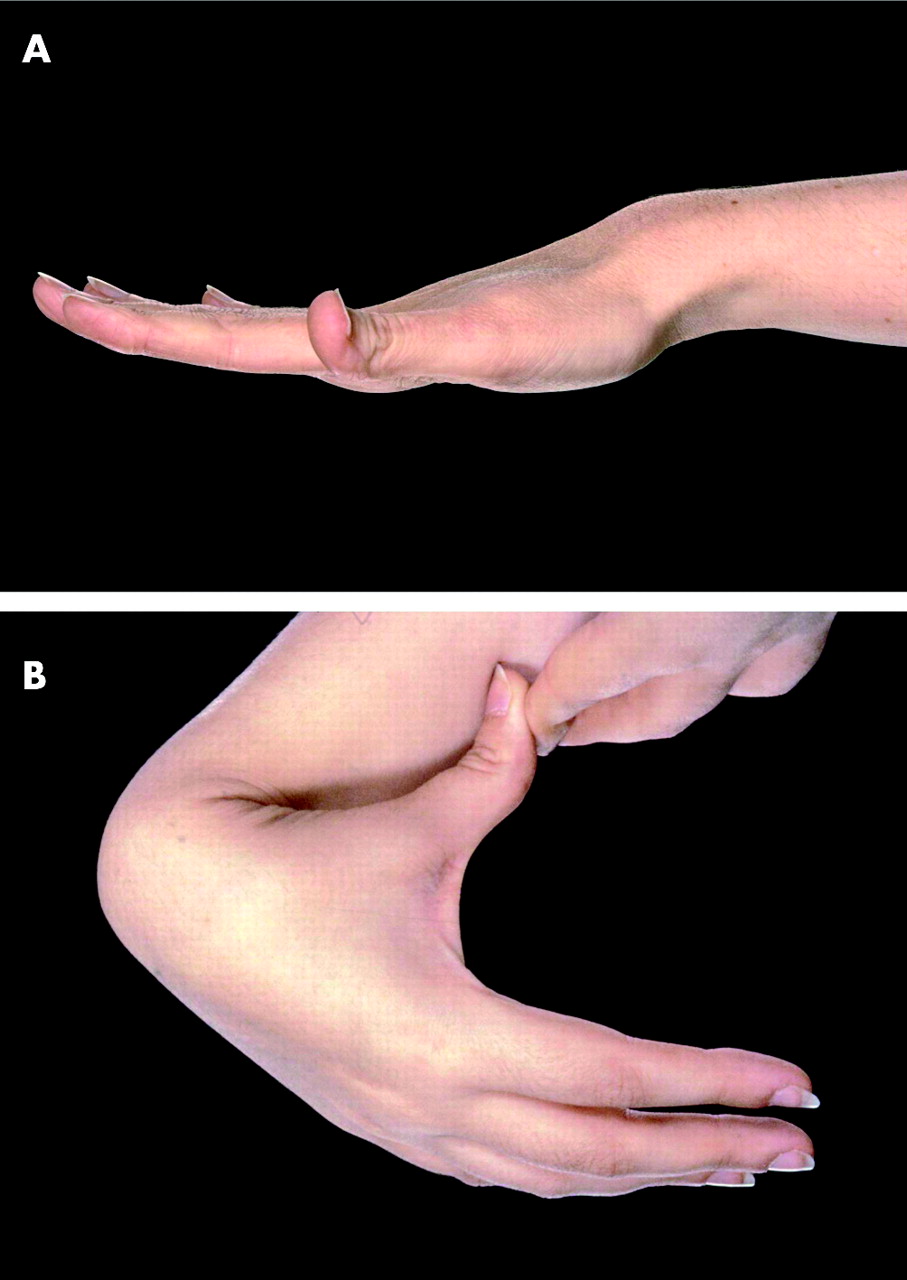
Stickler Syndrome Type 2
Stickler syndrome type 2. Beals syndrome is caused by a mutation in a gene that helps build connective tissue called fibrillin-2. Mutations in several genes cause the different types of Stickler syndrome. Ehlers Danlos syndrome EDS is a group of hereditary connective tissue disorders which manifests clinically with skin hyperelasticity hypermobility of joints atrophic scarring and fragility of blood vesselsIt is largely diagnosed clinically although identification of the gene encoding the collagen or proteins interacting with it is necessary to identify the type of EDS.
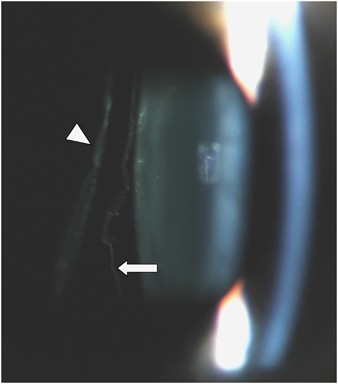
The eyes and some forms of Stickler may have severe and progressive near-sightedness myopia cataracts retinal detachment. Marshall syndrome is a genetic disorder of the connective tissue 2 which can cause hearing loss. This syndrome occurs when antibodies interfere with electrical impulses between the nerve and muscle cells.
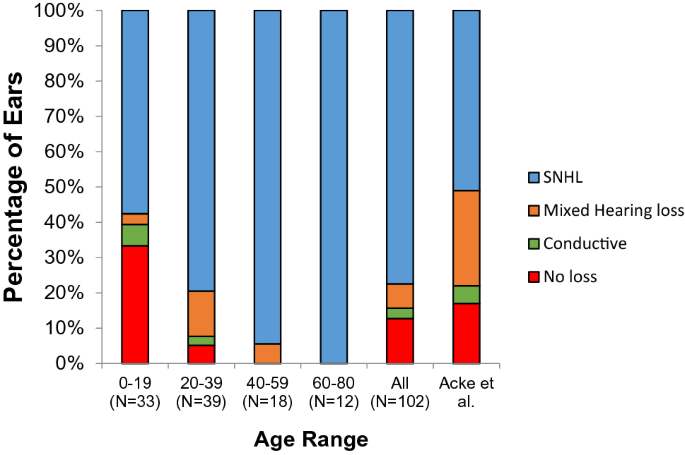
Hearing loss may be conductive sensorineural or mixed and may be progressive. It may be associated with other autoimmune diseases or more commonly coincide. Each chapter in GeneReviews is written by one or more experts on the specific condition or disease.
These mutations cause loss of function of the COL2A1 gene. Often this will be a medical geneticist. Online Medical Dictionary and glossary with medical definitions n listing.
Marshall syndrome which may be a variant of Stickler syndrome is also caused by COL11A1 gene mutations. The initial presentation can be similar to. The neuromuscular junction is the site where nerve cells meet muscle cells and help activate the muscles.
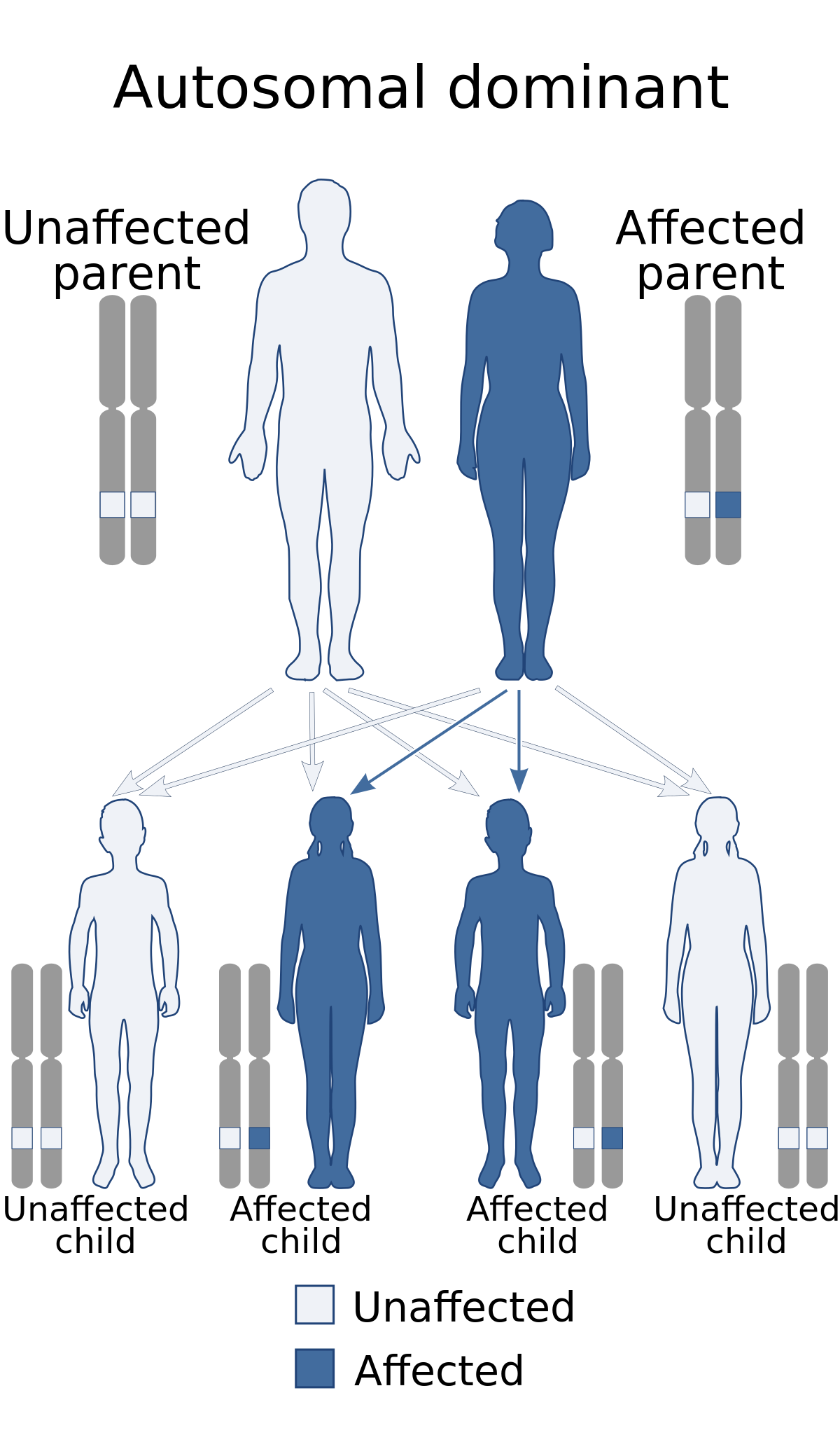
Sticklers syndrome An autosomal dominant hereditary progressive connective tissue disorder. 1 South India in particular has a high prevalence of PACG ranging from 05 to 275. For broad panel testing on connective tissue disorders please.
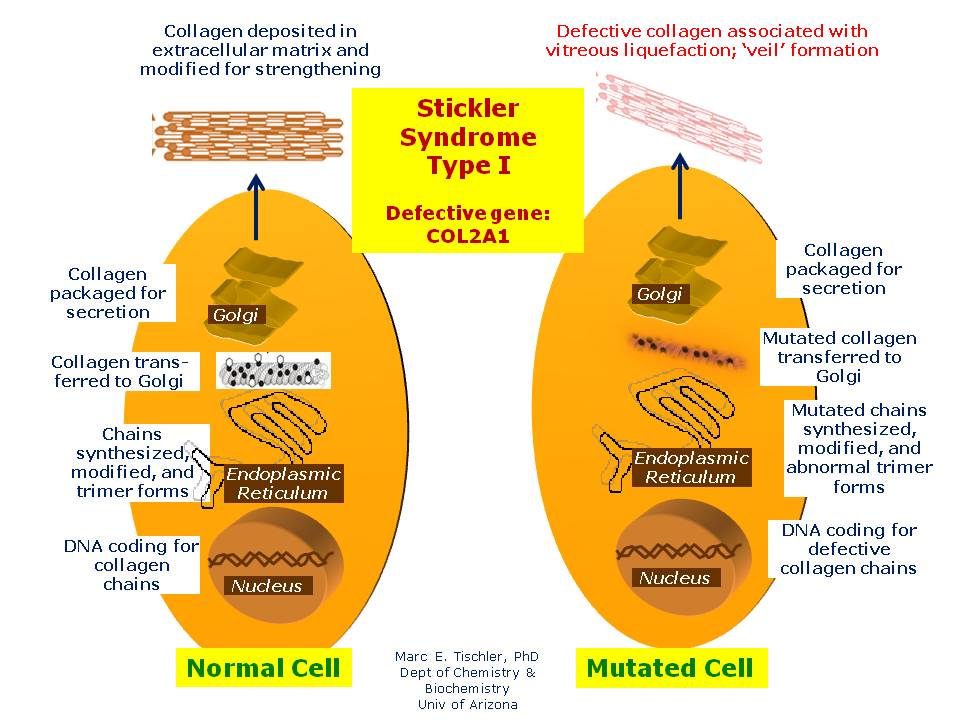
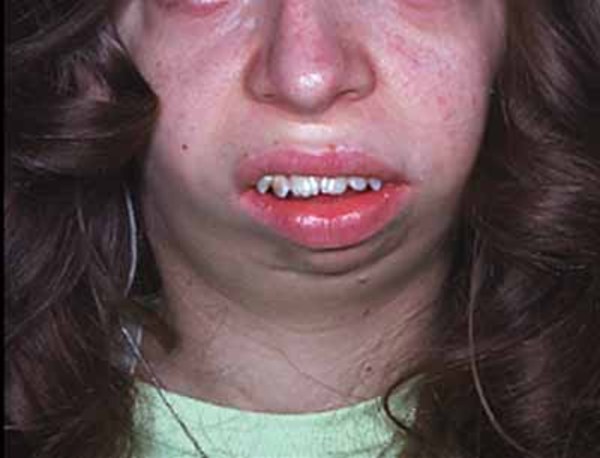
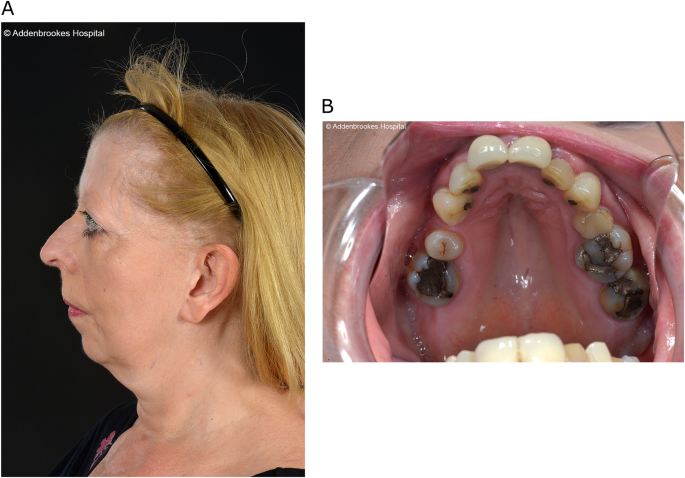
2-6 Angle closure is known to be highly heritable with family history being an important risk. Stickler syndrome type I STL1 is responsible for approximately 70 of reported cases and presents with a wide variety of symptoms affecting the eye ear facial appearance palate and musculoskeletal system and occurs due to mutations over the entire COL2A1 gene on chromosome 12q1311.
Marshall syndrome and Stickler syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
For broad panel testing on connective tissue disorders please. The eyes and some forms of Stickler may have severe and progressive near-sightedness myopia cataracts retinal detachment. Sticklers syndrome An autosomal dominant hereditary progressive connective tissue disorder. Each chapter in GeneReviews is written by one or more experts on the specific condition or disease. These mutations cause loss of function of the COL2A1 gene. Hearing loss may be conductive sensorineural or mixed and may be progressive. Online Medical Dictionary and glossary with medical definitions s listing. Loeys-Dietz syndrome is a genetic disorder of the bodys connective tissue. Beals syndrome is caused by a mutation in a gene that helps build connective tissue called fibrillin-2.
It is closely related to the gene fibrillin-1 that causes Marfan syndrome. It may be associated with other autoimmune diseases or more commonly coincide. Between 80 and 90 percent of all cases are classified as type I and are caused by mutations in the COL2A1 gene. The neuromuscular junction is the site where nerve cells meet muscle cells and help activate the muscles. Beals syndrome is also known as congenital contractural arachnoldactyly CCA which refers to the joint contractures shortening that are key features of the syndrome. Sticklers syndrome An autosomal dominant hereditary progressive connective tissue disorder. 1 South India in particular has a high prevalence of PACG ranging from 05 to 275.


























Post a Comment for "Stickler Syndrome Type 2"